Discover what a Diagnostic Adult Hearing Assessment is and why it’s crucial for your hearing health. Learn about the exam process and its insights on our blog!
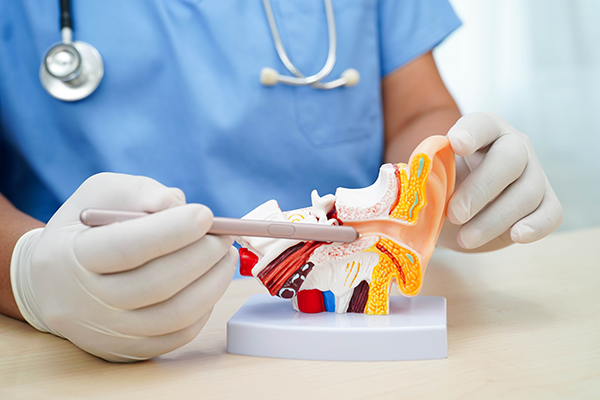
What is a diagnostic adult hearing assessment?
A diagnostic adult hearing assessment is a structured clinical exam used to measure hearing health, detect hearing loss, and recommend treatment. It involves multiple tests performed by an audiologist using specialised equipment in a sound-treated environment.
What does the hearing test include?
The hearing exam process begins with a medical and hearing history, followed by several core procedures that assess ear function, hearing sensitivity, and speech understanding. Results are used to guide a personalised care plan.
| Step | Purpose | Tool Used |
|---|---|---|
| Case history | Identify risk factors and symptoms | Interview |
| Otoscopic exam | Inspect ear canal and eardrum | Otoscope |
| Pure-tone audiometry | Measure hearing threshold levels | Audiometer + Headphones |
| Speech audiometry | Evaluate speech recognition ability | Audiometer + Word lists |
| Tympanometry | Assess middle ear pressure and function | Tympanometer |
| Acoustic reflex testing | Check involuntary muscle response to sound | Reflex decay equipment |
What are the key hearing tests?
Each one plays a role in identifying the type and cause of hearing loss.
- Pure-tone audiometry: Measures the softest sounds you can hear at different pitches; identifies conductive, sensorineural, or mixed hearing loss.
- Speech audiometry: Assesses how well you understand spoken words at various volumes; evaluates speech clarity and auditory processing.
- Tympanometry: Examines eardrum movement in response to air pressure; detects fluid, infections, or middle ear dysfunction.
- Acoustic reflex testing: Tests how ear muscles respond to loud sounds; helps pinpoint the location and type of hearing loss.
What does the evaluation show?
A hearing evaluation identifies the type and severity of hearing loss using measurable data.
Types of hearing loss include:
| Type | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Conductive | Blockage or damage in outer/middle ear | Earwax, fluid, otosclerosis |
| Sensorineural | Damage to inner ear or auditory nerve | Aging, noise exposure, ototoxic medications |
| Mixed | Combination of conductive and sensorineural | Chronic infections with inner ear damage |
What are the symptoms of hearing loss?
Common hearing problem symptoms include:
- Difficulty hearing in noisy settings
- Frequently asking people to repeat themselves
- Turning up the volume on devices
- Misunderstanding conversations
Why is early testing important?
Early identification through a comprehensive hearing test improves treatment outcomes. It enables timely intervention, such as hearing aid consultation, medical treatment, or lifestyle changes to prevent further loss.
When should adults get tested?
Adults should have a routine hearing test every 3–5 years starting at age 50, or sooner if symptoms appear. High-risk groups include those exposed to loud noise, certain medications, or chronic illnesses.
What happens after the diagnosis?
Following a hearing diagnosis, the audiologist provides a personalised hearing plan, which may include:
- Hearing aid evaluation
- Referral to an ENT
- Auditory training
- Regular follow-up hearing care
How can hearing tests improve quality of life?
A professional hearing test supports long-term hearing care by restoring communication ability, reducing social isolation, and improving cognitive health. Scheduling a hearing test appointment is the first step toward better hearing.