Discover what tympanometry is and why audiologists rely on this simple test daily. Gain insights into its importance for hearing health in our blog.
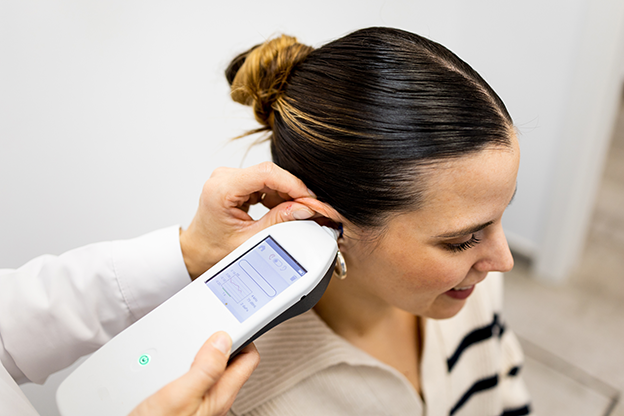
What is tympanometry?
Tympanometry is a 2-minute, non-invasive test that evaluates middle ear function by measuring eardrum movement in response to air pressure. It is used by audiologists and ENT specialists for routine hearing evaluations and middle ear diagnostics.
How does tympanometry work?
The tympanometry test uses a handheld probe that seals the ear canal and changes air pressure while emitting a sound. The probe records:
- Tympanic membrane mobility
- Ear canal volume
- Middle ear compliance
The resulting tympanogram shows how effectively the eardrum moves, helping identify middle ear abnormalities.
What does tympanometry measure?
Tympanometry measures 5 core values that reflect middle ear status:
| Measurement | Description |
|---|---|
| Tympanic pressure | Air pressure behind the eardrum |
| Compliance | Flexibility of the tympanic membrane |
| Ear canal volume | Space between probe tip and eardrum |
| Acoustic immittance | Resistance to sound flow in the middle ear |
| Acoustic reflex threshold | Response of middle ear muscles to loud sounds |
Each metric aids in diagnosing middle ear disorders, such as Eustachian tube dysfunction or otitis media.
What are tympanogram types?
Tympanograms are categorized into 3 standard types, each indicating different ear conditions:
| Type | Tympanogram Shape | Meaning | Common Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Peak near 0 daPa | Normal ear pressure and mobility | Healthy middle ear |
| Type B | Flat curve | Minimal movement, no peak | Fluid in ear, e.g., otitis media |
| Type C | Negative peak | Poor pressure equalization | Eustachian tube dysfunction |
When is tympanometry used?
Tympanometry is recommended for over 6 core diagnostic scenarios, including:
- Hearing screenings during routine exams
- Pediatric tympanometry for detecting recurrent infections
- Adult tympanometry for evaluating pressure changes or hearing loss
- ENT hearing tests during comprehensive audiometric assessments
It helps evaluate conductive, sensorineural, and mixed hearing loss by distinguishing middle ear dysfunction from inner ear issues.
What are tympanometry’s benefits?
Tympanometry offers 5 main clinical advantages that make it essential in diagnostic audiology:
- Takes under 2 minutes
- Non-invasive and painless
- Detects ear infections early
- Safe for children and adults
- Improves hearing loss treatment plans
These benefits streamline patient care and support accurate hearing evaluations.
What tools are used in tympanometry?
Tympanometry relies on digital audiology equipment that measures:
- Ear pressure changes
- Eardrum response amplitude
- Middle ear compliance
Commonly paired with pure tone audiometry and acoustic reflex testing, this equipment allows audiologists to conduct full hearing loss assessments quickly and effectively.
How are tympanometry results interpreted?
Audiologists interpret tympanometry results using tympanogram patterns and reference ranges. Key outcomes include:
- Normal range: Centered peak around 0 daPa
- Abnormal results: Flat or shifted curves requiring follow-up
If results indicate middle ear issues, patients are referred to otolaryngologists for further evaluation or otitis media treatment.
Why do audiologists rely on tympanometry?
Audiologists use tympanometry daily because it:
- Identifies early middle ear problems
- Supports accurate diagnosis of conductive hearing loss
- Assists in monitoring chronic ear conditions
- Enhances care for both pediatric and adult patients
This quick, reliable ear pressure test remains a cornerstone in diagnostic audiology and ENT clinics.






